
Multi Access Edge Computing (MEC)
The usage of MEC (Multi-Access Edge Computing) can be better understood by considering its meaning, as follows:

Multi-Access
A computing system that supports multiple types of connectivity, including LTE, 5G, Wi-Fi, and leased lines.

Edge
Relocating computing systems to the edge of the network—within the wireless or cellular network, so they are as close to end users as possible.

Computing
A computing system that supports applications requiring intensive processing and rapid, real-time responses to users.
Key Differences Between Public Cloud and MEC
Explore the connectivity diagram below to better understand the differences between using a traditional cloud and MEC.
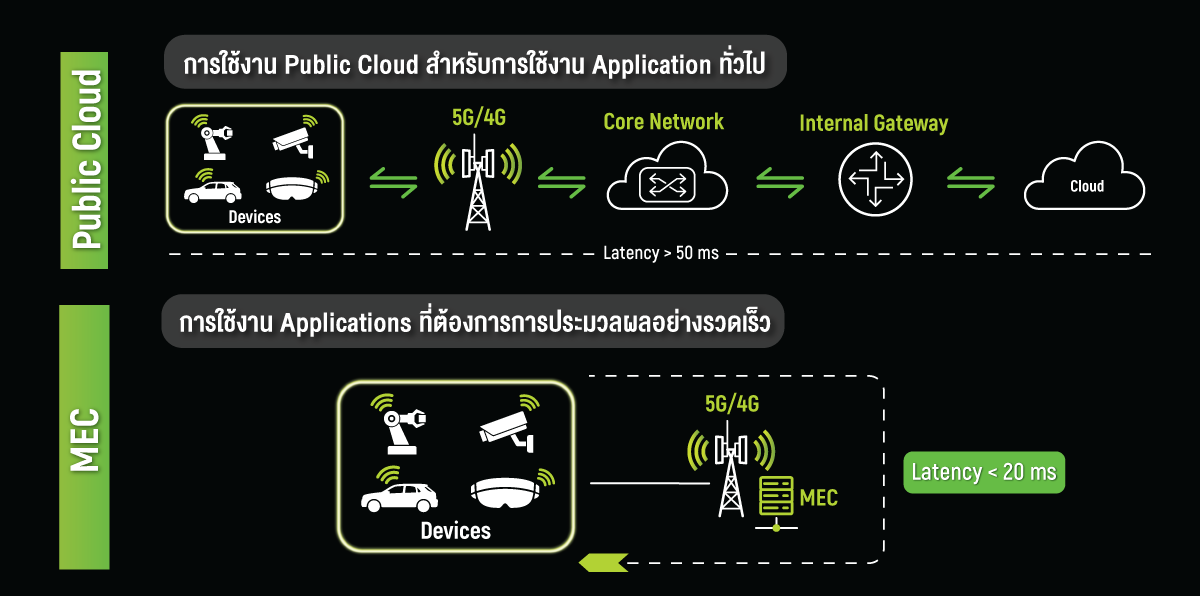
Running Applications on a Traditional Public Cloud
Running the application on a traditional public cloud showing that the data transmission must pass through multiple network layers and out to the internet before reaching the public cloud. This process introduces latency, resulting in higher delays compared to MEC.Therefore, traditional cloud usage is better suited for systems or applications focused on data storage or non-real-time processing, where immediate responses to users are not required. /p>
Running Applications on MEC
Using MEC by placing the computing architecture as close to the network as possible reduces data transmission latency to extremely low levels. When combined with 5G networks, MEC can achieve latency below 20 ms. This makes MEC highly suitable for systems or applications that require low latency, fast data processing, and real-time responsiveness to users.
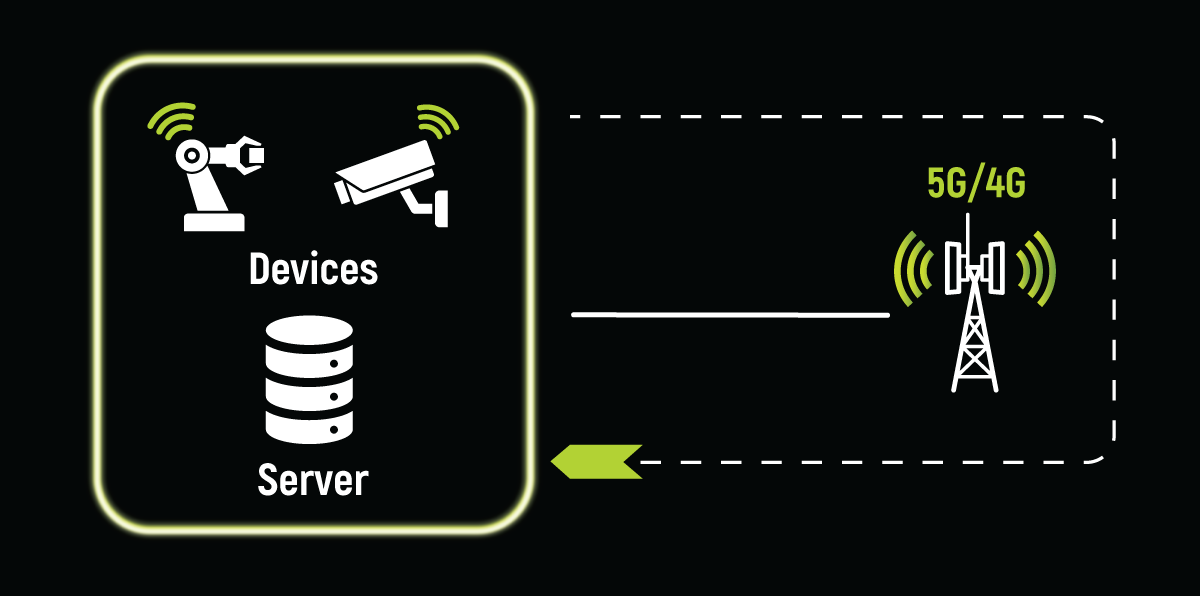
On Premise Server vs. MEC
Placing computing at the user’s location, such as deploying an on-premise server at the customer site, can indeed help reduce processing time and data transmission latency. However, there are several key differences between this approach and MEC, such as:
InvestmentUsing an on-premise server requires an up-front investment in hardware and software, as well as engineering staff to manage and maintain the system. In contrast, MEC operates under a service-based model similar to cloud services, where users pay based on usage and can shift the burden of managing and maintaining the infrastructure to the service provider.
Scalability : Although an on-premise server can technically scale up or down based on an organization’s needs, the actual process is often complex, time-consuming, and requires significant effort. In contrast, MEC is designed with high flexibility in scaling computing resources. Adjustments, whether increasing or reducing capacity, can be made easily through a centralized platform, enabling quick and convenient scaling aligned with real usage demands.
Security : Storing or processing data on an on-premise server within the organization provides a certain level of security. However, this depends heavily on the organization’s cybersecurity practices, including regular software updates to ensure systems remain modern and protected against cyber threats.
MEC also offers a high level of privacy and security, as data is processed close to the user. The connectivity can be designed with enhanced security measures to further strengthen data privacy. Additionally, MEC is built on established security standards and continuously receives cybersecurity updates from the service provider, ensuring strong and reliable data protection.
Application Use Cases Compatible with MEC
Key Benefits of MEC for Businesses
เรื่องราวความสำเร็จ และ เทคโนโลยี สร้างแรงบันดาลใจ
AIS 5G Solution: MEC
ระบบคลาวด์ให้เข้าใกล้ผู้ใช้งานมากที่สุด ช่วยให้สามารถใช้งานเครือข่ายด้วยการเข้าถึงแบบไร้สาย เพื่อให้บริการประมวลผลผ่านระบบคลาวด์ได้ในปริมาณมากและมีความปลอดภัยสูงสุด
Consult with our experts to discover the right solutions for your business.
You can contact AIS Business experts for professional consultation and digital technology planning to drive business growth immediately.
AIS Corporate Call Center
1149
© 2024 Advanced Info Service PLC. All rights reserved.














